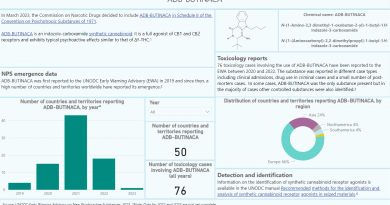
UNODC EWA: Number of NPS reported for the first time, at 10-years low
VIENNA, Austria – September 2023: In 2022, a total of 44 unique new psychoactive substances (NPS) have been reported for the first time to the UNODC Early Warning Advisory (EWA) on NPS, by 31 countries and territories. This represents a big decrease compared to 2021 when 87 substances were reported for the first time to the EWA and the lowest level of NPS reported for the first time for over ten years.
Out of the 44 NPS in 2022, synthetic cannabinoids were the largest group of NPS reported for the first time at the global level with 21 substances, followed by synthetic cathinones with 5 substances and fentanyl analogues with 4 substances.
Figure 1: New psychoactive substances reported for the first time from 2009 to 2022, by effect group
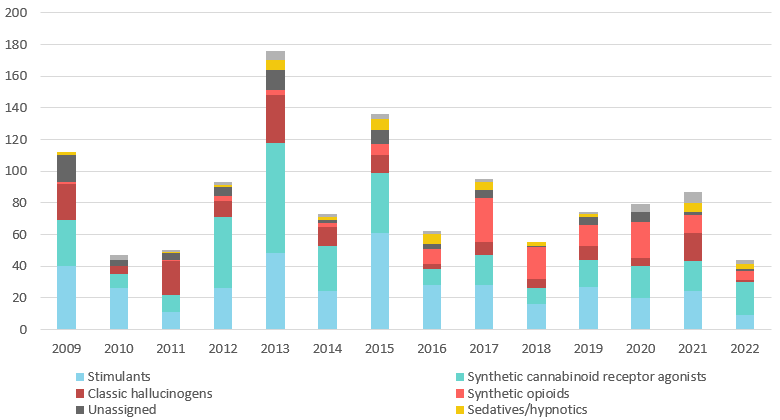
Source: UNODC Early Warning Advisory on New Psychoactive Substances, 2023.
In 2022 almost half of the substances reported for the first time were synthetic cannabinoids. These substances include derivatives of existing substances and a number of cannabinoids that seem to lack functional groups considered important for receptor binding activity e.g. ADB-INACA. More research is needed to demonstrate if these substances have cannabinoid receptor activity or could be considered as precursors. Other new substances reported in 2022 include hexahydrocannabinol and its acetate ester, both of which can be termed semi-synthetic cannabinoids as they can be manufactured from cannabidiol.
Figure 2: New psychoactive substances reported for the first time at the global level in 2022, by effect group
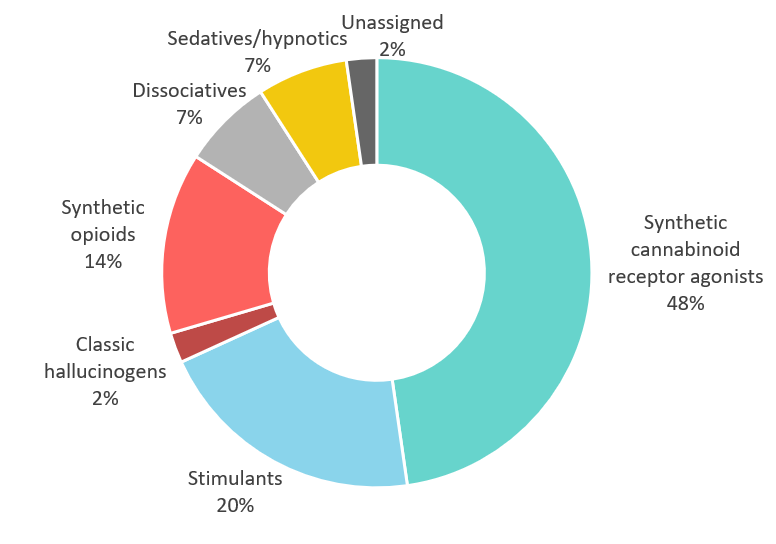
Source: UNODC Early Warning Advisory on New Psychoactive Substances, 2023.
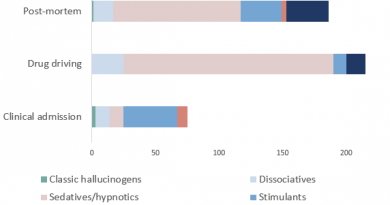
Note: Thirty-one reporter countries were included in 2022 and 32 reporter countries in 2021. Similarities in chemical structure do not always reflect identical psychoactive effects and a known psychoactive effect can be produced
by dissimilar chemical structures.
The emergence of new substances poses significant challenges to control efforts and health services. To assist the work of law enforcement, forensic drug testing and toxicology laboratories, UNODC provides analytical information on NPS in the UNODC EWA as well as assistance in the areas of quality assurance, provision of manuals and guidelines, field detection, and training. Moreover, information from the UNODC EWA contributes to identifying the most harmful, persistent and prevalent NPS as an important step towards prioritizing NPS for international review in the framework of the International Drug Control Conventions.
For further information, please see:
UNODC Early Warning Advisory – Publications
UNODC Laboratory and Scientific Services – Publications
UNODC Early Warning Advisory – Summary Dashboard